What is the key to open the door to the hidden mysteries? For Frodo and his fellow travelers in The Lord of the Rings trilogy, they needed to know the elvish answer to the riddle, “Speak friend and enter.” Gandalf knows this language, so they enter with ease. For years, the Egyptian hieroglyphics were unintelligible because we had no living person who knew the ancient language. After the discovery of the Rosetta Stone in Egypt with its three languages depicting the same text, the race was on to translate the pictographic writing.

In art school my fellow students and I worked in our shared studio classes daily, but sometimes we never made any progress. Then the day would come when the light bulb clicked on in one of our brains. When we took a break, instead of giving everyone’s work a cursory glance before going out for a snack, we would linger and take in the special magic of a unique vision. Where does this special insight come from? Is it a visitation from above? Or a piercing of the soul by divine artistic insight? Sometimes I think the rare and the strange shock us out of our ease and complacency.

Art historians divide Picasso’s early periods into his Blue Period (1901-1904), the Rose Period (1905-1907), the African-influenced Period (1908-1909), and Cubism (1909-1919). Some art historians call Picasso’s African Period his “Proto-Cubist” or primitive period. It lasted from 1907 to 1909. Picasso was 24 years old when he saw an exhibit of African art at the ethnographic museum at Palais du Trocadéro. He experienced a “revelation” and began to explore African art further. African masks and sculptures strongly influenced Picasso’s art for several years, when he began to paint in sculptural forms, earth tones, and in flattened sharpened shapes.

Pablo Picasso in his Montmartre Studio,1908, via The Guardian
Picasso had first seen an African mask at Gertrude Stein’s home. Recalling his visit to the Trocadéro Museum of Ethnology (now the Musée de l’Homme), Picasso said of the museum:
“A smell of mould and neglect caught me by the throat. I was so depressed that I would have chosen to leave immediately. But I forced myself to stay, to examine these masks, all these objects that people had created with a sacred, magical purpose, to serve as intermediaries between them and the unknown, hostile forces surrounding them, trying in that way to overcome their fears by giving them color and form. And then I understood what painting really meant. It’s not an aesthetic process; it’s a form of magic that interposes itself between us and the hostile universe, a means of seizing power by imposing a form on our terrors as well as on our desires. The day I understood this, I had found my path.”
That path led Picasso to what he called his “periode nègre” (black period) or African period. It lasted only a few years, to 1909, but it turned Picasso into an avid collector of African art, masks, and sculptures that inspired him for the rest of his career.

In our art class we chatted about how these masks inspired Picasso. Picasso used a palette of earthy tones, overlapping browns, and yellows with dark reds. By using Cubism, he explored a simplified geometry and the redefinition of perspectives. He tried to reveal objects from a different vantage point—from the mind, not only how the eyes perceive them. His Les Demoiselles d’Avignon signified a radical break from the naturalism that had defined Western art since the Renaissance, derailing former notions of what art was supposed to look like.
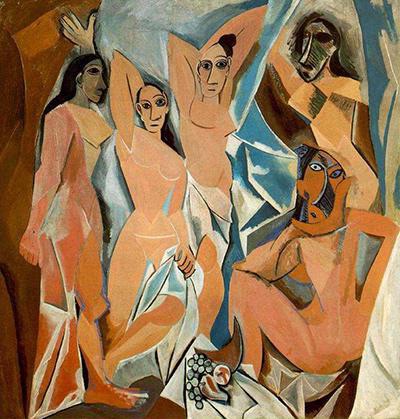
People criticized Picasso’s two-dimensional women as unfeminine, for their confrontational demeanor was a complete departure from the traditional depiction of female beauty. Artists and critics alike received the work negatively and saw its menacing sex workers as promiscuous and unfit for Paris salons. Picasso rolled up the canvas, considered scandalous even amongst his innermost circle, and stored it in his studio for years to come. Yet this groundbreaking painting influenced his future works.
As Thomas Merton wrote in No Man Is an Island:
“In an aesthetic experience, in the creation or the contemplation of a work of art, the psychological conscience is able to attain some of its highest and most perfect fulfillments. Art enables us to find ourselves and lose ourselves at the same time.”
Picasso broke through the accepted boundaries of Western culture and discovered his true spirit in through the voices of the ancestors speaking from the African past. He met the other and found himself. By bringing the African masks into his studio, Picasso lived out the message of Hebrews 13:2—
“Do not neglect to show hospitality to strangers, for by doing that some have entertained angels without knowing it.”
As artists today, who seek to find their own true self and unique voice, we must both find ourselves and lose ourselves. We must lose our preconceived notions of who we should be and discover our true selves. Some artists use this as license to be caricatures of an artist, but actual artists have work ethics because they have obligations to galleries and clients. Looking like an artist and being an artist are two different things. Finding our true selves is not only a task for creatives, but also a lifetime journey for all people engaged in spiritual growth. We all can recover the image of God, which is our true self, by both God’s grace and our cooperation in doing good to all.
We artists are not here to make pretty pictures, but to break down the boundaries between our walls that keep us estranged from God and neighbor. We are not as bold as Picasso! Most of us are not risk takers. Willingness to leap out in faith is what marks a famous artist. That same riskiness is what marks the prophets of the Bible. Prophets never praise the status quo, but remind the people of the nature of their God:
“For the LORD your God is God of gods and Lord of lords, the great God, mighty and awesome, who is not partial and takes no bribe, who executes justice for the orphan and the widow, and who loves the strangers, providing them food and clothing.” (Deuteronomy 10:17-18)
Isaiah 1:17 reminded the people of his day, “learn to do good; seek justice, rescue the oppressed, defend the orphan, and plead for the widow.” Jesus will pick up this same voice in Matthew 25:40, “And the king will answer them, ‘Truly I tell you, just as you did it to one of the least of these who are members of my family, you did it to me.’”
So how will we find our unique voice and creative expression today? The more we steep our heart and mind in the great spiritual writings of the ages, particularly those of whom have come through great suffering or difficulties, the closer we will come to understanding our own challenges in life. These hardships are not hurdles or barriers to our progress, but refiners of any weakness that needed to be strengthened.
As my teachers always said, “We test you, not to see how ignorant you are, but to see what we failed to teach well.”
I always liked their attitude better! I did not feel so dumb when I missed the right answer on their tests. I always liked art better, for more than one answer could be correct. If we work within the parameters of the assignment, we can interpret the art with our own vision and style.
Our recent class with the African masks was a big diversion from our usual method of working. First, the masks are from a different culture. They are as much of a culture shock to us as they were to Picasso. He had the privilege of buying them in the Parisian curio shops, so they sat around in his environment. We only had images. The mystery of these objects might not connect to us as they did to him.
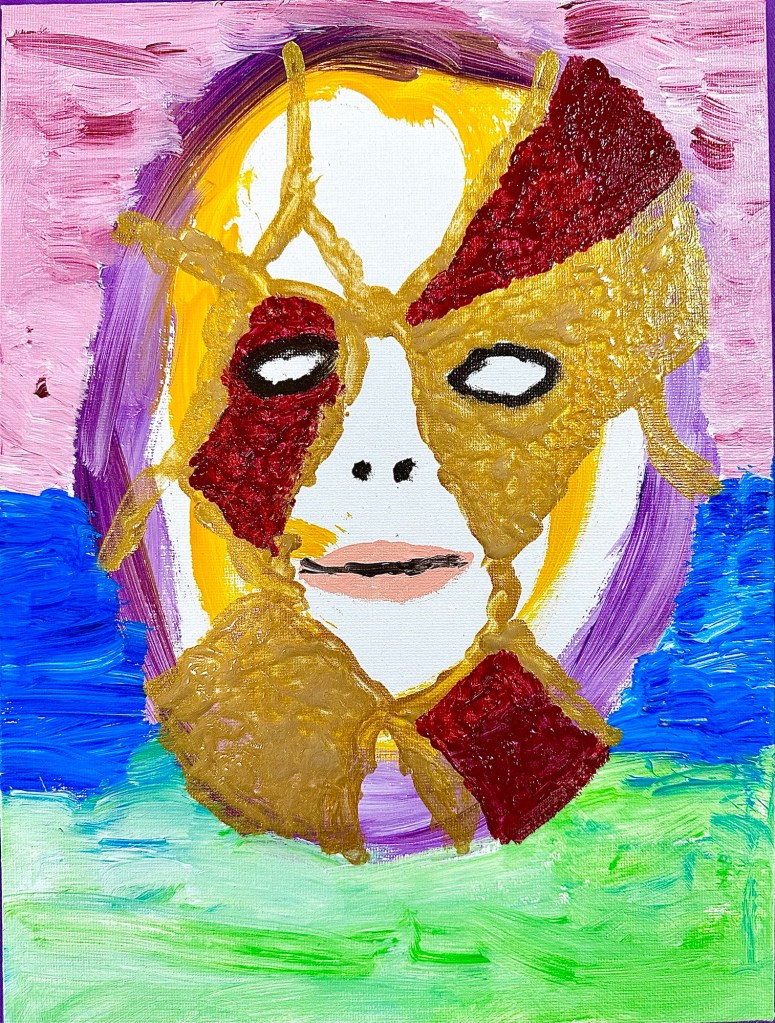

Mike brought several masks from his home collection. He decided to paint one that spoke to him. Like Picasso, he had an emotional connection to this mask. He made a successful rendering of the object before him. Unfinished, he would bring it back to the next class.

Tim worked on a mask representing his wife. He first painted his background with a dark wash, then began drawing a lighter design on top of it. The contrast of the dark and light without the middle tone was difficult for me to look at, but he seemed to be enjoying getting the big shapes down. I often let people work without jumping into change their activity. I figure they will learn more from going down a dead-end road by themselves than if I stop them before they go there. They will ask about this, and we will talk about it. They will not do it again. A little suffering leads to learning if we do no harm to the body.

Gail S. understood the concept of simplifying the faces into a mask. She chose a photo of herself and her granddaughter. With two mask shapes, she had multiple decisions to make. As with the others, her work was unfinished at the end of class.
This was a difficult and challenging lesson for everyone. Asking students to make an emotional connection and render the object also was aspirational. It also gave me an opportunity to see where they were on this learning journey. I will not issue this sort of challenge again for a while. I was afraid I had been boring them, but maybe not. I may need to bring brownies next Friday to make up to them. For some, they may be “grief snacks,” while for others, they will be “encouragement food.” If my bunged-up shoulder permits, I will indulge in grief baking. Otherwise, I will just eat the chocolate ice cream in my freezer, and ask for understanding.

I painted a Trump mask to get my emotions out and not have them bottled up inside. If we dislike an attribute in another person, it is because we have that attribute in our own life. I can get incredibly angry, but I bottle it up and it hurts me. I do not often let anyone else see it, so it can make me sick from holding it in. Whenever someone calls you a name, I remember the old song my parents taught me when I was a child:
“Sticks and stones may break my bones, but words will never hurt me.”
Anger is a difficult emotion for many people, especially for women. It is a “culturally unacceptable behavior,” for we have always expected strong emotions from men, but this expectation is changing over the generations. Proverbs 14:29 reminds all of us,
“Whoever is slow to anger has great understanding, but one who has a hasty temper exalts folly.”
The Old Testament often speaks of God’s anger, but this is because God’s people keep finding other gods to worship instead of the one true God. Psalms 145:8-9 reminds us of God’s true nature:
“The LORD is gracious and merciful, slow to anger and abounding in steadfast love.
The LORD is good to all, and his compassion is over all that he has made.”
The hidden mystery is in plain sight. It is the word of hope we hear: We are not sinners in the hand of an angry God. We are all beloved and God’s everlasting grace is redeeming us always. When things fall apart, God works to reframe and renew, even if we have difficulty recognizing God’s new creation or wanting to take part in God’s plans for the new heaven and the new earth.
Joy, peace, and recovery,
Cornelia
Historical Influence of African Art in the Modern Art Movement – ARTDEX
Pablo Picasso – Artists – Mnuchin Gallery
Stealing beauty | Art | The Guardian
https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2006/mar/15/art
Historical Influence of African Art in the Modern Art Movement – ARTDEX
Sticks And Stones May Break My Bones – Meaning & Origin of The Phrase
https://www.phrases.org.uk/meanings/sticks-and-stones-may-break-my-bones.html